Pipeline overview
6 Million
Patients Worldwide
1 Million
Patients in the U.S.
200,000
Global Deaths/Yr
No Fundamental Treatments
Current Option: L-DOPA
(Temporary Symptom Alleviation)
Major Symptoms
Tremor
Posture
Masked Face
Cognition
Current Approaches
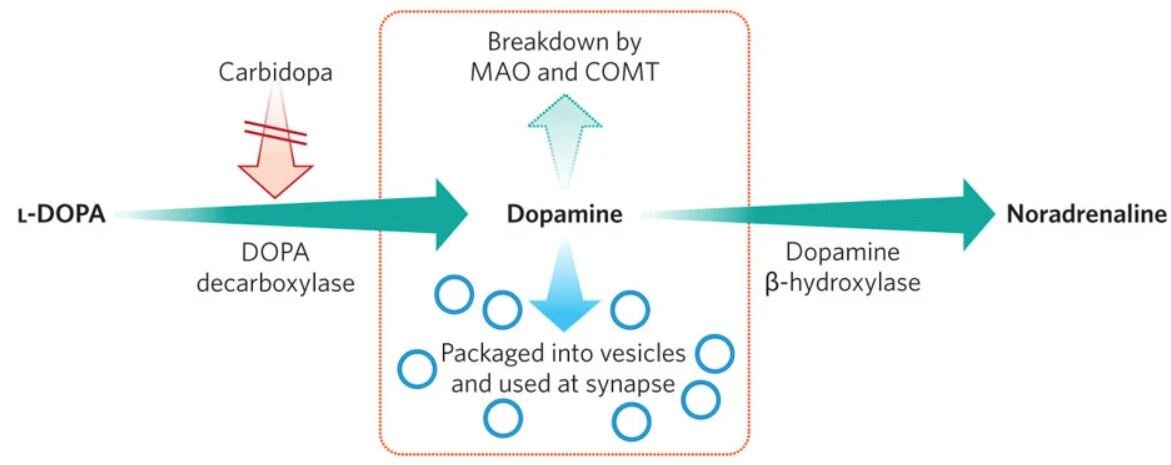
For Parkinson’s disease, the most commonly prescribed drugs are dopamine precursors.
Mode of action: Regulation of dopamine levels in the brain.
Major Drugs: Levodopa (L-DOPA) or dopamine agonists used with adjustments (for side effect reduction and complication management)
Unmet Needs: Fundamentally treat or delay the disease progress without serious side effects.
Photo: (Figure: I. Kang & J. M. Yoo et al., (2021) Nano Lett. 21, 2239-2346)
Market Size
2016: $3,041 million (estimated)
2018: $3,425 million (estimated)
2025: $6,679 million (estimated)
Biographene’s Approach to Parkinson’s Treatment
Mechanism of action: Dopamine concentration regulation.
The pathogenesis of Parkinson’s is multifactorial. However, we understand a-synucleinopathy – provoked by abnormal fibrillation (aggregation in fiber form) of a neuroprotein called a-synuclein is directly correlated to the loss of dopaminergic neurons.
At BioGraphene, we aim to rewrite the story of Parkinson’s disease by using graphene-based therapies to induce disaggregation of a-synuclein while also preventing further fibrillation from taking place.